Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) is rapidly transforming the way we interact with digital information, blending virtual content seamlessly into the physical world. While early AR applications relied heavily on device-based processing, the next major evolution is being driven by the AR Cloud – a powerful concept that acts as the shared digital memory of the world. As industries move toward spatial computing, the AR Cloud is emerging as the critical infrastructure that will define the future of immersive experiences.
Definition
AR Cloud refers to a shared, persistent digital layer mapped onto the physical world that enables augmented reality content to be accurately placed, anchored, and experienced across devices and users. It combines spatial mapping, computer vision, and cloud computing to create a continuously updated 3D representation of real environments. This allows digital objects and information to remain stable, interactive, and synchronized in real-world locations over time.
What Is the AR Cloud?
The AR Cloud refers to a persistent, shared, and spatially accurate digital layer mapped onto the real world and hosted in the cloud. Unlike traditional AR, which places temporary virtual objects into a user’s view, the AR Cloud enables digital content to exist at fixed, real-world locations that multiple users can access simultaneously and over time.
In simple terms, the AR Cloud allows virtual objects to “remember” where they are in the real world. A digital sign placed on a building today can still be seen tomorrow, by another user, from another device. This persistence and shared access are what make the AR Cloud revolutionary.
Core Components of the AR Cloud
Several advanced technologies work together to make the AR Cloud possible:
1. Spatial Mapping and Localization
At the heart of the AR Cloud is high-precision 3D mapping. Using cameras, sensors, and computer vision, real-world environments are scanned and converted into spatial maps. These maps allow AR systems to localize devices accurately within centimeters, ensuring virtual objects align perfectly with physical spaces.
2. Cloud Computing and Storage
Because spatial maps and persistent content are data-heavy, they are stored and processed in the cloud. Cloud infrastructure enables real-time updates, scalability, and cross-device compatibility, making AR experiences accessible on smartphones, AR glasses, and future wearables.
3. AI and Computer Vision
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in recognizing surfaces, objects, and environments. AI-powered computer vision allows AR systems to understand context – such as walls, floors, or landmarks – making interactions more natural and intelligent.
4. Networking and Multi-User Synchronization
The AR Cloud supports shared experiences, meaning multiple users can see and interact with the same virtual content in real time. This requires low-latency networking and precise synchronization, especially for collaborative or social AR applications.
Why the AR Cloud Matters
The AR Cloud is more than just a technical upgrade – it represents a shift in how digital information integrates with the physical world.
Persistent Digital Content:
With persistence, AR becomes a long-term medium rather than a fleeting experience. Digital notes, art, navigation cues, and information layers can remain anchored to locations indefinitely.
Shared Reality:
The AR Cloud enables a shared digital reality, where people see the same virtual objects in the same place. This opens the door to collaborative workspaces, multiplayer AR games, and social interactions that blend seamlessly with real environments.
Platform Independence:
Because the AR Cloud lives in the cloud, experiences are no longer tied to a single device or app. Users can switch devices while maintaining continuity, which is essential for enterprise and consumer adoption.
Real-World Use Cases of the AR Cloud
The impact of the AR Cloud spans across multiple industries:
Retail and E-Commerce:
Retailers can place persistent AR product displays in physical stores or public spaces. Customers can view product details, promotions, or virtual try-ons that remain consistent for all visitors.
Navigation and Smart Cities:
AR Cloud-powered navigation can overlay real-time directions, points of interest, and infrastructure data onto city streets. This is especially valuable for tourists, urban planners, and smart city initiatives.
Education and Training:
Educational institutions can create location-based AR lessons, such as historical reconstructions or science visualizations, that students can explore collaboratively.
Gaming and Entertainment:
AR Cloud gaming enables large-scale, location-based multiplayer experiences where the virtual world evolves over time, creating deeper immersion and community engagement.
Enterprise and Industry:
From remote maintenance to collaborative design, enterprises can use AR Cloud environments to share spatial data, instructions, and visualizations across teams and locations.
Challenges Facing the AR Cloud
Despite its potential, the AR Cloud faces several challenges:
Privacy and Security:
Mapping the physical world raises concerns about data ownership, surveillance, and user privacy. Secure data handling and transparent policies are essential for public trust.
Standardization:
Currently, multiple companies are building their own AR Cloud platforms. Lack of open standards may lead to fragmentation, limiting interoperability between systems.
Scalability and Accuracy:
Maintaining up-to-date, accurate spatial maps at a global scale is technically complex. Changes in physical environments must be continuously detected and updated.
The Future of the AR Cloud
As AR hardware becomes lighter, more affordable, and more powerful, the AR Cloud will become increasingly central to everyday digital interactions. Future developments may include:
- Global-scale AR maps accessible across platforms
- AI-driven contextual AR, adapting content based on user behavior and environment
- Integration with the metaverse, blending physical and virtual worlds seamlessly
- AR glasses as primary interfaces, reducing reliance on smartphones
The AR Cloud will likely become as fundamental as GPS or the internet itself – a background infrastructure powering countless applications without users even noticing.
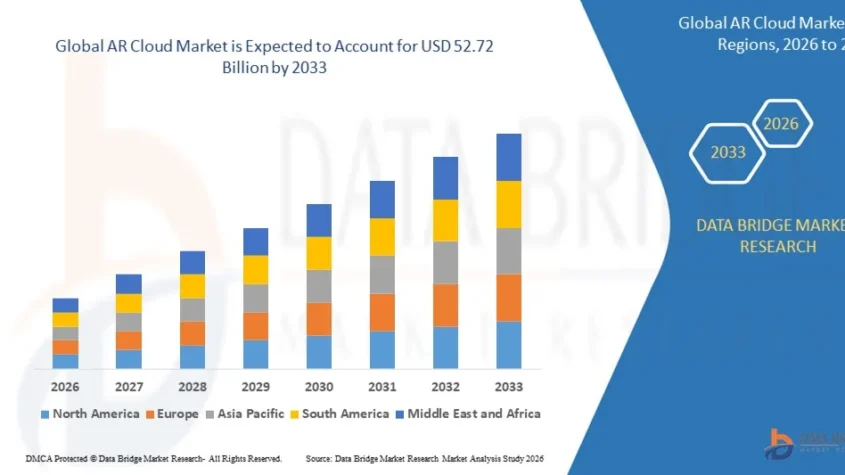
Growth Rate of AR Cloud Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the worldwide AR cloud market was estimated at USD 7.07 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.55% to reach USD 52.72 billion by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-ar-cloud-market
Conclusion
The AR Cloud is the invisible foundation that will unlock the full potential of augmented reality. By enabling persistent, shared, and intelligent digital content in the real world, it transforms AR from isolated experiences into a connected spatial web. As technology continues to evolve, the AR Cloud will redefine how we learn, work, shop, play, and interact with our surroundings.
Discover Modern Comfort: A Guide to Apartment Rent in Beirut
Beirut, the lively capital of Lebanon, is a city that blends deep-rooted history with a mo…